Maps form a key part of the common operating picture during an event. Crisisworks mapping enables users to interact with the maps without the need to learn to use complex Geographical Information Systems (GIS) software. A GIS can still be used in conjunction with the system for more detailed information if such technical resources are available.
There are two components of Crisisworks mapping:
- Mapping User Interface (UI) Maps - used to navigate using the mapAsset databases , view and filter geospatial data
- Assets - used for storing, maintaining and resolving addresses and locality information
Maps are used throughout Crisisworks. However different features are used in different screens including:
- Registers - Requests, Recovery (People & Property), etc
- Dashboards & projector views
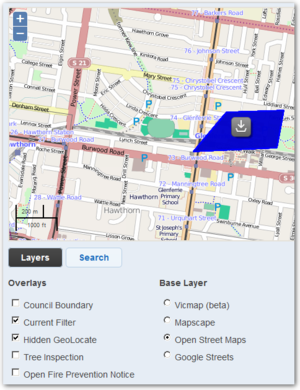
Maps provide key information relevant to the event. In register views, the maps only show records from the currently selected filter. Maps are also used to capture optional geographical information when Requests, Recovery Cases and other register records are added or edited.
On this page
| Table of Contents | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
The mapping user interface
The map user interface (UI) provides an easy way to locate records by their address/location and get an overview of affected areas.
The default map view is called the base layer. The base layer comprises a set of map tiles and defines what is viewed in terms of cartography - streets, landmarks and terrain.
Crisisworks supports switching base layers and each has their own look and benefits, though they all share the same navigation interface.The following section explains how to navigate and use the map.
| Warning |
|---|
The Hybrid devices such as the Windows Surface Pro has have a touch screen and behaves like a mobile device. Use touch gestures such as drag and pinch by directly touching the screen to manipulate the map, just like mobile devices. |
...
To move the map around, use the hand tool to click and drag the map across the view window in any direction you desire.
Desktop Computers
On desktopsdesktop computers, hold the mouse button in the map view window and a hand icon will appear. Drag the map across the view window in any direction you desire.
...
Searching assets by name
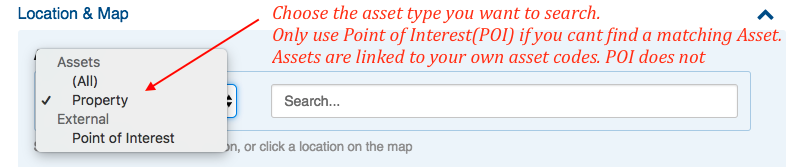
To search assets by name
- Select the asset type, as shown in this image
- Type an asset name into the asset search box
- Assets are displayed in a pulldown list (see image below)
- If a map is also configured for that view, the assets are also drawn onto the map
- You can refine your results by selecting a type (type such as Property, Parcel and Point of Interest are common for governmental users)
- "All" will search all asset types at the same time
- If a type is selected with a configured just-in-time lookup, then that external lookup will be performed. This is typically the case for "Point of Interest" searches.
- Some forms have additional property details that can also be entered, such as the locally known name such as Woolies, or Jo's Cafe
- If you need to change the selected asset press the red X as shown here
Find nearest assets
The Find Nearest Assets feature provide a quick way to list nearby assets without setting a filter (see also Assets; Filters).
...
Adding external layers to Crisisworks
As an alternative to importing data into Crisisworks, external layers can be configured for live external overlays onto Crisisworks maps.
KML file format
Keyhole Markup Language (KML) is an interoperable international standard notation for Internet mapping which is based on XML and is compatible with Google maps used in Crisisworks. Use this format for adding layers representing information that change infrequently (ie. Municipal boundaries, 1-in-100 year flood extent etc). The latest versions of MapInfo and ArcGIS are capable of exporting to this format. Shapefiles can be converted using tools such as shape2ge. Google Earth Pro can also be used for editing and managing KML files. Note: use of these third party tools are not supported
Crisisworks accepts only valid KML files with a .kml extension and does not accept KMZ (.kmz) archives or any other variant of KML. It can only process the one KML file and although it is possible to upload an archive, the map layer will not display.
GeoRSS feed
GeoRSS is an emerging standard for encoding locations into web feeds and is also in XML, however can be accessed via a simple URL. The advantage of GeoRSS is that it can be read and updated in near real-time and can be provided by third parties. Use this format for adding layers representing information that changes (ie. Weather data, current fire boundaries etc).
The RSS parser complies with the RSS 2.0 standard. It is important that your feed validates to this standard in order to function properly as a map layer.
...